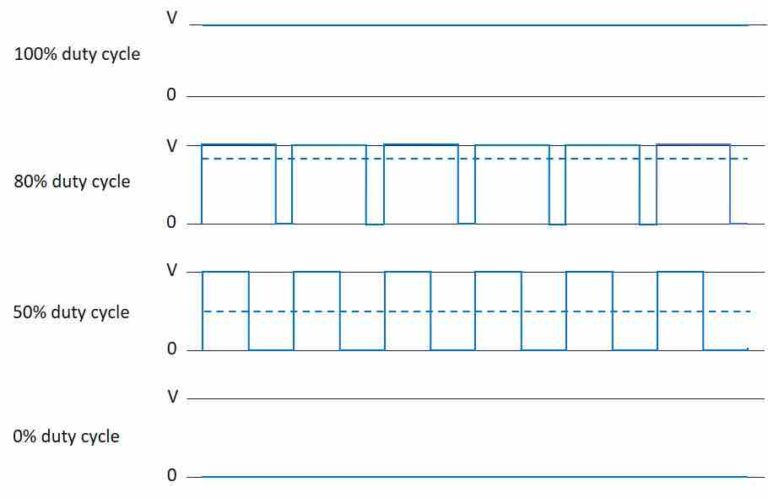
Basics of Motor Control Circuits Circuit Diagram Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a powerful and widely-used technique in modern electrical engineering, particularly for controlling the speed of DC motors and optimizing power conversion. By adjusting the width of the pulses in a signal, PWM allows for efficient control of motor performance, delivering precise regulation of motor speed and torque. PWM or pulse width modulation applies to square wave signals of voltages and current. In a square wave voltage signal, there are only two values for the voltage level: the HIGH(Vcc) and LOW(ground - 0). Square wave signals are periodic and has a constant frequency of operation. Duty Cycle and Pulse Width

Also the amplitude of the motor voltage remains constant so the motor is always at full strength. The result is that the motor can be rotated much more slowly without it stalling. So how can we produce a pulse width modulation signal to control the motor. Easy, use an Astable 555 Oscillator circuit as shown below. PWM, short for Pulse Width Modulation, is an important concept in modern electronics. It is generally used as a power delivery mechanism in motor control and lighting control systems. You can easily modify the above circuit to control the speed of a DC Motor. Related Posts: Low Power Audio Amplifier using 555 Timer; PWM LED Dimmer Using Projects using these devices need a varying voltage to control the position, brightness, or speed of the device. But most microcontrollers are unable to generate this varying analog voltage. Pulse width modulation is used to simulate this varying analog voltage using a digital microcontroller or timer. How Pulse Width Modulation Works

Basic (PWM) Motor Speed Control Using 555 Timer ICs Circuit Diagram
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) has several key parts that show how signals work and affect devices. Knowing these parts is key for better performance in things like motor control, LED dimming, and making audio signals. Duty Cycle. The PWM Duty Cycle is very important for controlling the power sent to a device. It shows how long the signal is high The objective of this design project is to develop and prototype a high efficiency pulse width modulation (PWM) speed control for a small DC motor. A block diagram of the overall system is shown below: Figure 1. Block diagram of the PWM DC motor speed control Background: A pulse-width modulation signal begins with a voltage that goes up and down repeatedly. The classic method of creating the oscillation is with a resistor-capacitor (RC) circuit. This circuit uses RC timing with a diode twist to alter the ratio of the on-pulse time versus the off-pulse time (called "duty cycle").